Which of the Following Can Be Used as a Reference During a Mobile Device Update Process?

Hardware-side view of a typical smartphone
The features of mobile phones are the fix of capabilities, services and applications that they offer to their users. Mobile phones are oftentimes referred to as characteristic phones, and offer basic telephony.[ clarification needed ] Handsets with more avant-garde calculating power through the utilise of native code attempt to differentiate their own products past implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers. This has led to bully innovation in mobile phone evolution over the past 20 years.
The mutual components found on all phones are:
- A number of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated excursion (IC) fries.
- A battery (typically a lithium-ion battery), providing the power source for the phone functions.
- An input mechanism to allow the user to interact with the phone. The most common input mechanism is a keypad, simply touch screens are also establish in smartphones.
- Basic mobile telephone services to allow users to make calls and send text letters.
- All GSM phones use a SIM card to let an account to exist swapped amidst devices. Some CDMA devices too have a similar bill of fare called a R-UIM.
- Individual GSM, WCDMA, IDEN and some satellite phone devices are uniquely identified by an International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number.
All mobile phones are designed to work on cellular networks and contain a standard set of services that allow phones of different types and in different countries to communicate with each other. However, they can also support other features added by various manufacturers over the years:
- roaming which permits the aforementioned phone to be used in multiple countries, providing that the operators of both countries have a roaming agreement.
- send and receive information and faxes (if a computer is attached), admission WAP services, and provide full Net admission using technologies such as GPRS.
- applications like a clock, alarm, calendar, contacts, and calculator and a few games.
- Sending and receiving pictures and videos (by without internet) through MMS, and for brusque distances with e.g. Bluetooth.
- In Multimedia phones Bluetooth is unremarkably but important Feature.
- GPS receivers integrated or continued (i.e. using Bluetooth) to cell phones, primarily to aid in dispatching emergency responders and road tow truck services. This characteristic is more often than not referred to as E911.
- Button to talk, available on some mobile phones, is a feature that allows the user to be heard only while the talk button is held, similar to a walkie-talkie.
- A hardware notification LED on some phones.
MOS integrated excursion chips [edit]
A typical smartphone contains a number of metallic–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated excursion (IC) chips,[1] which in turn comprise billions of tiny MOS field-outcome transistors (MOSFETs).[2] A typical smartphone contains the post-obit MOS IC fries.[1]
- Application processor (CMOS system-on-a-bit)
- Flash retention (floating-gate MOS retentivity)
- Cellular modem (baseband RF CMOS)
- RF transceiver (RF CMOS)
- Phone camera image sensor (CMOS image sensor)
- Power management integrated circuit (power MOSFETs)
- Brandish driver (LCD or LED driver)
- Wireless communication chips (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS receiver)
- Sound scrap (audio codec and power amplifier)
- Gyroscope
- Capacitive touchscreen controller (ASIC and DSP)[1] [iii] [4]
- RF power amplifier (LDMOS)[5] [6] [7]
User interface [edit]

Too the number keypad and buttons for accepting and failing calls (typically from left to correct and coloured greenish and cherry respectively), push button mobile phones unremarkably characteristic two option keys, ane to the left and one to the right, and a four-directional D-pad which may characteristic a center push button which acts in resemblance to an "Enter" and "OK" push.
A pushable curl cycle has been implemented in the 1990s on the Nokia 7110.
Software, applications and services [edit]
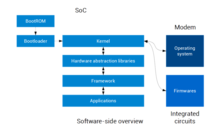
Software-side view of a typical smartphone
In early stages, every mobile telephone company had its own user interface, which can be considered as "closed" operating system, since in that location was a minimal configurability. A limited variety of bones applications (unremarkably games, accessories like calculator or conversion tool and then on) was usually included with the phone and those were not available otherwise. Early mobile phones included basic web browser, for reading bones WAP pages. Handhelds (Personal digital assistants like Palm, running Palm Os) were more sophisticated and as well included more advanced browser and a impact screen (for use with stylus), but these were non broadly used, comparison to standard phones. Other capabilities similar Pulling and Pushing Emails or working with agenda were also made more accessible but it ordinarily required physical (and not wireless) Syncing. BlackBerry 850, an email pager, released January 19, 1999, was the commencement device to integrate Email.
A major step towards a more "open" mobile Os was the symbian S60 OS, that could exist expanded past downloading software (written in C++, java or python), and its appearance was more configurable. In July 2008, Apple introduced its App store, which made downloading mobile applications more accessible. In October 2008, the HTC Dream was the first commercially released device to utilize the Linux-based Android Bone, which was purchased and farther developed past Google and the Open Handset Alliance to create an open competitor to other major smartphone platforms of the time (Mainly Symbian operating system, BlackBerry OS, and iOS)-The operating system offered a customizable graphical user interface and a notification system showing a listing of recent messages pushed from apps.
The virtually unremarkably used data application on mobile phones is SMS text messaging. The first SMS text message was sent from a reckoner to a mobile phone in 1992 in the Britain, while the offset person-to-person SMS from telephone to phone was sent in Republic of finland in 1993.
The outset mobile news service, delivered via SMS, was launched in Finland in 2000. Mobile news services are expanding with many organizations providing "on-demand" news services by SMS. Some also provide "instant" news pushed out by SMS.
Mobile payments were start trialled in Finland in 1998 when 2 Coca-Cola vending machines in Espoo were enabled to work with SMS payments. Eventually, the thought spread and in 1999 the Philippines launched the first commercial mobile payments systems, on the mobile operators Globe and Smart. Today, mobile payments ranging from mobile banking to mobile credit cards to mobile commerce are very widely used in Asia and Africa, and in selected European markets. Usually, the SMS services employ short lawmaking.
Some network operators take utilized USSD for data, amusement or finance services (e.g. M-Pesa).
Other non-SMS data services used on mobile phones include mobile music, downloadable logos and pictures, gaming, gambling, adult entertainment and advert. The starting time downloadable mobile content was sold to a mobile phone in Finland in 1998, when Radiolinja (at present Elisa) introduced the downloadable ringtone service. In 1999, Japanese mobile operator NTT DoCoMo introduced its mobile Cyberspace service, i-Mode, which today is the world'south largest mobile Internet service.
Even after the appearance of smartphones, network operators have continued to offer information services, although in some places, those services have become less common.
Power supply

Mobile telephone charging service in Republic of uganda

The world's v largest handset makers introduced a new rating system in November 2008 to help consumers more easily place the most energy-efficient chargers.[8]
Mobile phones more often than not obtain power from rechargeable batteries. There are a variety of ways used to charge cell phones, including USB, portable batteries, mains ability (using an Ac adapter), cigarette lighters (using an adapter), or a dynamo. In 2009, the first wireless charger was released for consumer utilize.[9] Some manufacturers accept been experimenting with culling power sources, including solar cells.[ten]
Various initiatives, such every bit the Eu Common External Power Supply take been announced to standardize the interface to the charger, and to promote energy efficiency of mains-operated chargers. A star rating system is promoted by some manufacturers, where the almost efficient chargers consume less than 0.03 watts and obtain a five-star rating.
Bombardment [edit]
Nearly modern mobile phones use a lithium-ion battery.[xi] [12] [13] A popular early on mobile telephone battery was the nickel metallic-hydride (NiMH) type, due to its relatively pocket-sized size and low weight. Lithium-ion batteries later became ordinarily used, as they are lighter and do not have the voltage depression due to long-term over-charging that nickel metal-hydride batteries practise. Many mobile phone manufacturers use lithium–polymer batteries equally opposed to the older lithium-ion, the main advantages beingness even lower weight and the possibility to make the battery a shape other than strict cuboid.[xiv]
SIM card [edit]

GSM mobile phones require a small-scale microchip called a Subscriber Identity Module or SIM carte, to function. The SIM bill of fare is approximately the size of a small postage stamp and is usually placed underneath the bombardment in the rear of the unit of measurement. The SIM deeply stores the service-subscriber key (IMSI) used to identify a subscriber on mobile telephony devices (such as mobile phones and computers). The SIM card allows users to modify phones by simply removing the SIM card from one mobile phone and inserting it into another mobile phone or broadband telephony device.
A SIM card contains its unique serial number, internationally unique number of the mobile user (IMSI), security hallmark and ciphering information, temporary information related to the local network, a listing of the services the user has access to and ii passwords (Pivot for usual use and PUK for unlocking).
SIM cards are available in three standard sizes. The first is the size of a credit carte (85.threescore mm × 53.98 mm x 0.76 mm, defined by ISO/IEC 7810 as ID-1). The newer, about popular miniature version has the same thickness but a length of 25 mm and a width of 15 mm (ISO/IEC 7810 ID-000), and has one of its corners truncated (chamfered) to prevent misinsertion. The newest incarnation known equally the 3FF or micro-SIM has dimensions of 15 mm × 12 mm. Most cards of the two smaller sizes are supplied every bit a total-sized card with the smaller carte du jour held in place by a few plastic links; it can easily be broken off to be used in a device that uses the smaller SIM.
The offset SIM card was made in 1991 by Munich smart menu maker Giesecke & Devrient for the Finnish wireless network operator Radiolinja. Giesecke & Devrient sold the kickoff 300 SIM cards to Elisa (ex. Radiolinja).
Those cell phones that do not use a SIM card have the information programmed into their memory. This data is accessed by using a special digit sequence to access the "NAM" every bit in "Proper noun" or number programming menu. From there, information can be added, including a new number for the phone, new Service Provider numbers, new emergency numbers, new Authentication Key or A-Key code, and a Preferred Roaming List or PRL. However, to preclude the phone being accidentally disabled or removed from the network, the Service Provider typically locks this data with a Chief Subsidiary Lock (MSL). The MSL also locks the device to a particular carrier when it is sold as a loss leader.
The MSL applies only to the SIM, so once the contract has expired, the MSL withal applies to the SIM. The telephone, still, is also initially locked by the manufacturer into the Service Provider'due south MSL. This lock may be disabled so that the phone can use other Service Providers' SIM cards. Most phones purchased outside the U.South. are unlocked phones because there are numerous Service Providers that are close to one some other or have overlapping coverage. The cost to unlock a telephone varies but is usually very cheap and is sometimes provided by independent phone vendors.
A like module called a Removable User Identity Module or RUIM card is present in some CDMA networks, notably in China and Indonesia.
Multi-card hybrid phones [edit]
A hybrid mobile phone tin take more than than one SIM carte, even of unlike types. The SIM and RUIM cards can be mixed together, and some phones also back up 3 or four SIMs.[15] [16]
From 2010 onwards they became popular in India and Indonesia and other emerging markets,[17] attributed to the desire to obtain the lowest on-net calling rate. In Q3 2011, Nokia shipped 18 million of its depression cost dual SIM telephone range in an endeavour to brand up lost basis in the higher finish smartphone market place.[18]
Display [edit]
Mobile phones take a display device, some of which are likewise touch screens. The screen size varies greatly by model and is usually specified either every bit width and height in pixels or the diagonal measured in inches.
Some mobiles have more than than one display, for example that mobileKyocera Echo, an Android smartphone with a dual 3.v inch screen. The screens can besides be combined into a single iv.7 inch tablet style figurer.[nineteen]
Primal processing unit [edit]
Mobile phones have central processing units (CPUs), like to those in computers, but optimised to operate in low ability environments. In smartphones, the CPU is typically integrated in a organisation-on-a-chip (SoC) application processor.
Mobile CPU functioning depends not only on the clock rate (more often than not given in multiples of hertz)[20] only also the memory hierarchy besides profoundly affects overall functioning. Because of these issues, the performance of mobile phone CPUs is often more appropriately given by scores derived from diverse standardized tests to measure the real effective performance in unremarkably used applications.
Miscellaneous features [edit]
Other features that may be found on mobile phones include GPS navigation, music (MP3) and video (MP4) playback, RDS radio receiver, built-in projector, vibration and other "silent" ring options, alarms, memo recording, personal digital banana functions, ability to watch streaming video, video download, video calling, congenital-in cameras (1.0+ Mpx) and camcorders (video recording), with autofocus[ dubious ] and wink, ringtones, games, PTT, memory card reader (SD), USB (2.0), dual line support, infrared, Bluetooth (2.0) and WiFi connectivity, NFC, instant messaging, Internet e-mail service and browsing and serving as a wireless modem.
The outset smartphone was the Nokia 9000 Communicator[ dubious ] in 1996 which added PDA functionality to the bones mobile phone at the time. As miniaturization and increased processing ability of microchips has enabled ever more features to exist added to phones, the concept of the smartphone has evolved, and what was a high-terminate smartphone five years ago, is a standard phone today.
Several phone series accept been introduced to accost a given market segment, such as the RIM BlackBerry focusing on enterprise/corporate customer email needs; the SonyEricsson Walkman serial of musicphones and Cybershot series of cameraphones; the Nokia Nseries of multimedia phones, the Palm Pre the HTC Dream and the Apple tree iPhone.
Nokia and the University of Cambridge demonstrated a bendable cell telephone called the Morph.[21] Some phones have an electromechanical transducer on the back which changes the electrical voice signal into mechanical vibrations. The vibrations flow through the cheek basic or brow allowing the user to hear the conversation. This is useful in the noisy situations or if the user is difficult of hearing.[22]
As of 2018, there are smartphones that offer opposite wireless charging.[23]
Multi-mode and multi-ring mobile phones [edit]
Nearly mobile phone networks are digital and use the GSM, CDMA or iDEN standard which operate at diverse radio frequencies. These phones tin can only be used with a service plan from the same visitor. For example, a Verizon phone cannot be used with a T-Mobile service, and vica versa.
A multi-mode telephone operates across different standards whereas a multi-band phone (also known more specifically every bit dual, tri or quad ring) mobile phone is a phone which is designed to work on more than one radio frequency. Some multi-mode phones can operate on analog networks as well (for example, dual band, tri-style: AMPS 800 / CDMA 800 / CDMA 1900).
For a GSM telephone, dual-band usually means 850 / 1900 MHz in the United States and Canada, 900 / 1800 MHz in Europe and most other countries. Tri-band means 850 / 1800 / 1900 MHz or 900 / 1800 / 1900 MHz. Quad-ring means 850 / 900 / 1800 / 1900 MHz, also called a globe phone, since it can work on any GSM network.
Multi-band phones have been valuable to enable roaming whereas multi-mode phones helped to introduce WCDMA features without customers having to surrender the wide coverage of GSM. Well-nigh every unmarried true 3G telephone sold is actually a WCDMA/GSM dual-mode mobile. This is likewise true of 2.75G phones such as those based on CDMA-2000 or EDGE.
Challenges in producing multi-mode phones [edit]
The special challenge involved in producing a multi-fashion mobile is in finding ways to share the components between the different standards. Manifestly, the telephone keypad and display should be shared, otherwise it would exist hard to treat as one phone. Beyond that, though, there are challenges at each level of integration. How hard these challenges are depends on the differences between systems. When talking well-nigh IS-95/GSM multi-mode phones, for example, or AMPS/IS-95 phones, the base band processing is very different from system to system. This leads to real difficulties in component integration then to larger phones.
An interesting special example of multi-way phones is the WCDMA/GSM phone. The radio interfaces are very different from each other, but mobile to core network messaging has stiff similarities, pregnant that software sharing is quite like shooting fish in a barrel. Probably more than importantly, the WCDMA air interface has been designed with GSM compatibility in heed. It has a special style of operation, known as punctured way, in which, instead of transmitting continuously, the mobile is able to stop sending for a short period and try searching for GSM carriers in the area. This mode allows for safe inter-frequency handovers with channel measurements which tin can only be approximated using "airplane pilot signals" in other CDMA based systems.
A final interesting case is that of mobiles roofing the DS-WCDMA and MC-CDMA 3G variants of the CDMA-2000 protocol. Initially, the chip rate of these phones was incompatible. As part of the negotiations related to patents, it was agreed to use compatible chip rates. This should mean that, despite the fact that the air and arrangement interfaces are quite different, even on a philosophical level, much of the hardware for each arrangement inside a phone should be common with differences being mostly confined to software.
Information communications [edit]
Mobile phones are now heavily used for data communications. such as SMS messages, browsing mobile web sites, and even streaming audio and video files. The principal limiting factors are the size of the screen, lack of a keyboard, processing ability and connection speed. Most cellphones, which supports data communications, tin be used as wireless modems (via cable or bluetooth), to connect computer to internet. Such access method is slow and expensive, merely it can be bachelor in very remote areas.
With newer smartphones, screen resolution and processing power has become bigger and better. Some new phone CPUs run at over 1 GHz. Many circuitous programs are now available for the various smartphones, such as Symbian and Windows Mobile.
Connectedness speed is based on network back up. Originally information transfers over GSM networks were possible only over CSD (circuit switched data), it has bandwidth of 9600 chip/s and usually is billed past connection time (from network point of view, it does not differ much from vocalization call). Subsequently, there were introduced improved version of CSD - HSCSD (high speed CSD), it could utilise multiple time slots for downlink, improving speed. Maximum speed for HSCSD is ~42 kbit/s, it also is billed by time. Later was introduced GPRS (general packet radio service), which operates on completely different principle. It too can utilise multiple fourth dimension slots for transfer, but it does not tie up radio resources, when not transferring information (as opposed to CSD and like). GPRS unremarkably is prioritized nether vocalisation and CSD, and then latencies are big and variable. Later on, GPRS was upgraded to Edge, which differs mainly by radio modulation, squeezing more than data capacity in same radio bandwidth. GPRS and EDGE ordinarily are billed by data traffic book. Some phones also feature full Qwerty keyboards, such as the LG enV.
As of Apr 2006, several models, such every bit the Nokia 6680, support 3G communications. Such phones have access to the Web via a free download of the Opera web browser. Verizon Wireless models come with Net Explorer pre-loaded onto the phone.
Vulnerability to viruses [edit]
As more circuitous features are added to phones, they get more than vulnerable to viruses which exploit weaknesses in these features. Fifty-fifty text messages can be used in attacks past worms and viruses.[24] Avant-garde phones capable of e-mail tin be susceptible to viruses that tin can multiply by sending messages through a phone'southward address book.[ citation needed ] In some telephone models, the USSD was exploited for inducing a mill reset,[25] resulting in clearing the data and resetting the user settings.
A virus may allow unauthorized users to access a telephone to observe passwords or corporate data stored on the device. Moreover, they can be used to commandeer the phone to make calls or ship messages at the owner's expense.[ citation needed ]
Mobile phones used to have proprietary operating system unique only to the manufacturer which had the beneficial effect of making information technology harder to blueprint a mass attack. Even so, the ascension of software platforms and operating systems shared past many manufacturers such every bit Java, Microsoft operating systems, Linux, or Symbian OS, may increase the spread of viruses in the future.
Bluetooth is a characteristic now plant in many college-end phones, and the virus Caribe hijacked this function, making Bluetooth phones infect other Bluetooth phones running the Symbian Bone. In early November 2004, several spider web sites began offer a specific slice of software promising ringtones and screensavers for sure phones. Those who downloaded the software found that it turned each icon on the telephone's screen into a skull-and-crossbones and disabled their phones, so they could no longer ship or receive text messages or admission contact lists or calendars. The virus has since been dubbed "Skulls" by security experts. The Commwarrior-A virus was identified in March 2005, and it attempts to replicate itself through MMS to others on the telephone'due south contact list. Like Cabir, Commwarrior-A also tries to communicate via Bluetooth wireless connections with other devices, which tin can somewhen lead to draining the battery. The virus requires user intervention for propagation however.
Bluetooth phones are also subject to bluejacking, which although not a virus, does let for the transmission of unwanted messages from anonymous Bluetooth users.
Cameras [edit]
Most electric current phones as well have a built-in digital camera (see camera phone), that can take resolutions as high as 108M pixels. [26] This gives rise to some business concern about privacy, in view of possible voyeurism, for example in swimming pools. Republic of korea has ordered manufacturers to ensure that all new handsets emit a beep whenever a picture is taken.
Audio recording and video recording is often besides possible. Most people do not walk around with a video camera, just practice carry a phone. The inflow of video camera phones is transforming the availability of video to consumers, and helps fuel citizen journalism.
See also [edit]
- Mobile game
- Ringtone
- Smartphone
- Mobile phone form factor
- For more than in depth information about mobile telephone review you tin too reach out hare
- Wallpaper
-
 Telephones portal
Telephones portal
https://thenitintech.com [edit]
- ^ a b c Kim, Woonyun (2015). "CMOS power amplifier blueprint for cellular applications: an Border/GSM dual-mode quad-band PA in 0.xviii μm CMOS". In Wang, Hua; Sengupta, Kaushik (eds.). RF and mm-Wave Power Generation in Silicon. Academic Press. pp. 89–90. ISBN978-0-12-409522-9.
- ^ "Remarks by Managing director Iancu at the 2022 International Intellectual Holding Conference". United States Patent and Trademark Function. June 10, 2019. Archived from the original on 17 December 2019. Retrieved 20 July 2019.
- ^ Kent, Joel (May 2010). "Touchscreen technology basics & a new development". CMOS Emerging Technologies Briefing. CMOS Emerging Technologies Research. 6: 1–13.
- ^ Ganapati, Priya (5 March 2010). "Finger Fail: Why Most Touchscreens Miss the Point". Wired. Archived from the original on 11 May 2014. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ^ Baliga, Bantval Jayant (2005). Silicon RF Power MOSFETS. World Scientific. pp. i–2. ISBN9789812561213.
- ^ Asif, Saad (2018). 5G Mobile Communications: Concepts and Technologies. CRC Press. p. 134. ISBN9780429881343.
- ^ "LDMOS Products and Solutions". NXP Semiconductors . Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- ^ Sheen, James (22 October 2009). "Coming together 30mW Standby in Mobile Telephone Chargers". Electronic Products. Archived from the original on 18 July 2010. Retrieved four November 2009.
- ^ goingcellular.com — Powermat wireless charger now available
- ^ Charge Use Mini Solar Panel | Android Phones.
- ^ Williams, R. Grand.; Darwish, M. Northward.; Blanchard, R. A.; Siemieniec, R.; Rutter, P.; Kawaguchi, Y. (2017). "The Trench Power MOSFET—Part II: Application Specific VDMOS, LDMOS, Packaging, and Reliability". IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices. 64 (three): 692–712. doi:10.1109/TED.2017.2655149. ISSN 0018-9383.
- ^ "IEEE Medal for Ecology and Safety Technologies Recipients". IEEE Medal for Environmental and Safety Technologies. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ^ "Keywords to agreement Sony Energy Devices – keyword 1991". Sony Energy Devices Corporation. Sony. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ "Cell Phone Bombardment Guide". Archived from the original on eleven June 2010. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ Example of a Triple SIM hybrid phone.
- ^ The Latest F160 Quad Sim Quad Standby TV Java Telephone with Qwerty Keyboard | Tri Sim Phones.
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20110429/wr_nm/us_handsets Archived May 8, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Nokia boosted past sales of cheap handsets". October twenty, 2011.
- ^ Kyocera Echo Telephone Review | PCWorld.
- ^ "CPU Frequency". CPU Globe Glossary. CPU World. 25 March 2008. Retrieved one Jan 2010.
- ^ Reardon, Marguerite. "Nokia demos bendable cell phone". CNET News, February 25, 2008. Retrieved xx July 2009.
- ^ Mito 228: Unique Handphone, Can Hear with the cheek Archived 2011-10-17 at the Wayback Car, IeuMart.com
- ^ Sohail, Omar (October 16, 2018). "Huawei Takes a Jab at Apple - Says Its Mate 20 Pro Volition Be Able to Accuse iPhones Wirelessly".
- ^ "How Cell-phone Viruses Work". HowStuffWorks. 2005-ten-04. Retrieved 2021-01-21 .
- ^ "'Dirty USSD' code could automatically wipe your Samsung TouchWiz device (updated)". Engadget.
- ^ "Oppo Reno 10x zoom - Full phone specifications". grand.gsmarena.com.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_phone_features
0 Response to "Which of the Following Can Be Used as a Reference During a Mobile Device Update Process?"
Post a Comment